Intrapartum Care
Duration = 8:28
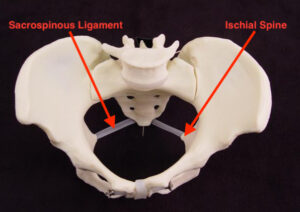
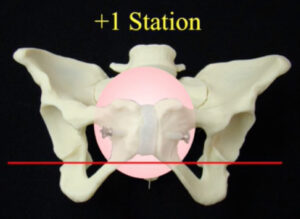
I believe the video is a little unclear about the exact location of the ischial spines. Here are a couple of images that I hope will clarify their location and clinical use.
00:00
APGO educational topic number eleven
00:02
intrapartum care meet la florida live
00:05
which she is a gravida one pair zero at
00:07
39 weeks estimated gestational age and
00:10
we are going to follow her through the
00:11
process of a normal labor and delivery
00:13
the learning objectives are to
00:15
differentiate between the signs and
00:17
symptoms of true and false labor perform
00:19
the initial assessment of a laboring
00:21
patient describe the four stages of
00:23
labor and recognize common abnormalities
00:25
explain pain management approaches
00:27
during labor describe methods for
00:29
monitoring the mother and fetus describe
00:32
the steps of a vaginal delivery list
00:34
indications for operative delivery and
00:36
finally identify maternal risks specific
00:39
to delivery in developing countries
00:41
labora is at home feeling contractions
00:44
and she’s not sure if she’s in true or
00:45
false labor what is the definition of
00:47
labor let’s check our smart device the
00:50
definition of labor requires that two
00:52
things need to occur number one painful
00:55
uterine contractions and number two
00:56
cervical dilation at term many women
01:00
will feel spontaneous contractions which
01:01
they describe as tightening of the
01:03
uterus if they are not causing cervical
01:05
dilation then they are referred to as
01:06
Braxton Hicks contractions labora is on
01:09
the phone with her OB provider and she’s
01:11
trying to decide whether she should come
01:12
in to be evaluated on labor and delivery
01:14
what does the OB provider recommend come
01:17
in if you have leakage of fluid bleeding
01:19
painful contractions every five minutes
01:22
for one hour or decrease in fetal
01:24
movements laborious contractions are
01:27
every five minutes and they happen for
01:29
one hour so she and her partner head to
01:31
labor and delivery
01:31
in triage laborious prenatal records
01:34
will be reviewed and a focused history
01:36
will be performed let’s review the
01:39
assessments unique to pregnancy and
01:41
labor and delivery we need to assess
01:43
both maternal and fetal status fetal
01:46
heart tones are usually assessed with a
01:47
fetal heart monitor we also need to know
01:50
fetal presentation whether the fetuses
01:52
vertex or breech assess with either an
01:54
abdominal ultrasound or by exam since we
01:56
need to assess whether labora is in
01:58
labor we need to perform a sterile
01:59
vaginal examination we described three
02:01
components from this exam we assess the
02:03
cervical dilation the effacement and the
02:05
fetal station will first discuss
02:08
cervical dilation and effacement here is
02:11
the uterus and the cervix with the
02:13
internal
02:13
and the external loss the cervix will
02:15
dilate and this refers to the opening of
02:17
the internal loss complete dilation is
02:19
10 centimeters the cervix will also
02:22
undergo a Faceman which means that it
02:23
will thin out or the distance between
02:25
the internal and the external
02:27
awesome marked by the screen error will
02:29
become zero a non effaced cervix is
02:31
about four centimeters this green dotted
02:34
line shows a cervix that is about 50%
02:36
thinned out or will be about two
02:38
centimeters and this pink dotted line
02:41
shows a completely effaced cervix that
02:43
is zero centimeters thick moving on to
02:45
fetal station station describes the
02:48
fetal presenting part usually the vertex
02:50
in relation to the issue of spines which
02:51
are palpable vaginally when the
02:53
presenting parts at the level of the
02:54
ischial spines it is zero station as the
02:57
vertex descends down the pelvis the
02:59
station passes plus one plus two all the
03:01
way to plus five these divisions
03:02
represent centimeters below the ischial
03:04
spines on the other hand a minus one
03:07
station would meet the vertex was still
03:08
one centimeter above the ischial spine
03:10
minus 2 station would be 2 centimeters
03:12
above etc labora is found to be 5
03:15
centimeters dilated 80% effaced and 0
03:18
station so she is now admitted to labor
03:20
and delivery we described four stages of
03:22
labor the first stage of labor is from
03:25
the onset of labor to full cervical
03:27
dilation stage one is further divided
03:29
into the latent phase and the active
03:31
phase labora is already passed the
03:33
latent phase which includes from
03:34
cervical dilation to about 4 centimeters
03:37
and can be variable in length the active
03:39
phase starts at about 4 centimeters
03:41
dilated and there should be more rapid
03:43
and predictable cervical dilation the
03:45
latent phase can last for days whereas
03:47
the cervix should dilate at
03:49
approximately 1.2 to 1.5 centimeters per
03:52
hour in the active phase stage 2 is from
03:54
complete dilation to delivery of the
03:56
infant stage 3 is from delivery of the
03:59
infant to delivery of the placenta stage
04:02
4 is the immediate postpartum period of
04:04
approximately two hours after delivery
04:05
of the placenta labora is in the active
04:08
phase of stage 1 of labor walking is
04:10
generally more comfortable than laying
04:12
supplying there is decreased GI
04:14
peristalsis so patients should limit
04:15
their solid food intake for this can
04:17
lead to nausea and vomiting fetal
04:20
well-being is monitored during labor by
04:22
measurement of the fetal heart tones
04:23
which can be done by either electronic
04:25
fetal monitoring or intermittent oskol
04:27
an external toka motor is used to assess
04:29
uterine activity labor would like for us
04:32
to start discussing pain management
04:33
options during labor labor results
04:35
severe pain for most women during stage
04:38
1 of labor pain results from the
04:40
contractions of the uterus and dilation
04:42
of the cervix resulting in visceral pain
04:44
at the levels of T 10 to l1 as labor
04:47
progresses the fetal head distance the
04:49
lower birth canal and perineum resulting
04:51
in somatic pain transmitted through s2
04:53
to s4 some patients tolerate the pain of
04:56
labor and delivery without any need for
04:58
medications for women who opt for pain
05:00
relief during labor we have many safe
05:02
effective methods the epidural block is
05:04
the most effective form of intrapartum
05:06
pain relief in the United States local
05:08
anesthetic or narcotics are infused
05:10
through a catheter into the epidural
05:12
space this lasts during labor and
05:14
delivery and can be individually
05:15
titrated IV opioids and opioid agonist
05:19
and antagonist can also be used however
05:21
since they are systemically administered
05:23
the primary mechanism of pain relief is
05:25
via a sedation labora is now completely
05:28
dilated at 10 centimeters and is now in
05:30
stage 2 of Labor
05:31
how long do women push once they are
05:34
completely dilated for women who have
05:36
not had a vaginal delivery pushing
05:38
usually takes about two to three hours
05:39
the length is shorter if the woman has
05:41
not received an epidural if a woman has
05:44
already had one vaginal delivery the
05:46
second stage may be very short and she
05:48
may not need to push for very long since
05:51
this is laborious first delivery she
05:52
will likely need to push for 2 to 3
05:54
hours as a student you may stay in the
05:56
room to help with this pushing part of
05:58
stage 2 delivery of the fetus is
06:00
imminent when a half dollar size amount
06:02
of the fetal vertex is visible in
06:04
between pushes as the fetus crowns it is
06:07
helpful to support the perineum and
06:09
facilitate extension of the head after
06:11
delivery of the head there is
06:13
restitution then there is delivery of
06:16
the anterior shoulder then the delivery
06:19
of the posterior shoulder the optimum
06:21
place for baby after delivery is skin to
06:23
skin on the maternal chest next we’ll
06:25
move on to stage 3 active management of
06:28
the third stage of labor it decreases
06:30
the risk of postpartum hemorrhage this
06:32
involves bundle massage gentle core
06:34
traction and administration of IV or I
06:36
am oxytocin the placenta can take up to
06:39
30 minutes to do
06:41
there are two classic signs that the
06:42
placenta is separating from the uterus
06:44
one a gush of blood and two lengthening
06:47
of the umbilical cord after the placenta
06:50
delivers the uterus should be palpated
06:51
to ensure that it is firm and has
06:53
contracted and the placenta should be
06:55
visually examined to make sure it has
06:57
been completely removed moving now to
06:59
operative deliveries operative
07:01
deliveries are accomplished by applying
07:03
direct traction to the fetal skull with
07:05
forceps or by applying traction to the
07:07
fetal scalp with a vacuum extractor the
07:10
incidence of operative vaginal delivery
07:12
in the United States is estimated to be
07:13
approximately 3.5% the general
07:16
indications are one prolonged or
07:18
arrested second stage number two
07:20
suspicion of immediate or potential
07:22
fetal compromise and number three
07:24
shortening of the second stage for
07:26
maternal benefit our journey on to labor
07:28
and delivery with our patient labora has
07:30
assumed that we are in a high resource
07:32
setting in low resource settings there
07:34
are a multitude of risks of labor and
07:36
delivery and 99% of maternal deaths
07:38
occur in developing countries every day
07:41
800 women die from preventable causes
07:43
related to pregnancy and childbirth this
07:45
is the equivalent of two jumbo jets
07:47
daily more than half of these deaths
07:49
occur in sub-saharan Africa and another
07:51
one-third occur in Southeast Asia the
07:54
highest risk is for adolescent girls the
07:56
major complications that account for 75%
07:58
of maternal deaths are bleeding
08:00
infection high blood pressure
08:02
complications from delivery and unsafe
08:04
abortion this concludes the aapko video
08:06
on intrapartum care we reviewed normal
08:08
labor and delivery operative deliveries
08:10
and maternal risks specific to
08:12
developing countries
08:19
[Music]
