Transgender Care
Duration 10:23
Transgender Care
Plummer XD, Liang A
Clinical Case Applicability: reproductive endocrinology, hormone therapy, transgender care
Learning Objectives:
1. Understand the principles of sex hormone synthesis and regulation
2. Understand the mechanisms and pathways of hormone therapy
Clinical Presentation: transgender individuals often report gender incongruence throughout their lifetime that can occur before or after puberty.
How are sex steroids synthesized and regulated?
Regulation: the synthesis and secretion of estrogens and androgens are regulated by the HPO axis: hypothalamus GnRH anterior pituitary FSH/LH ovary
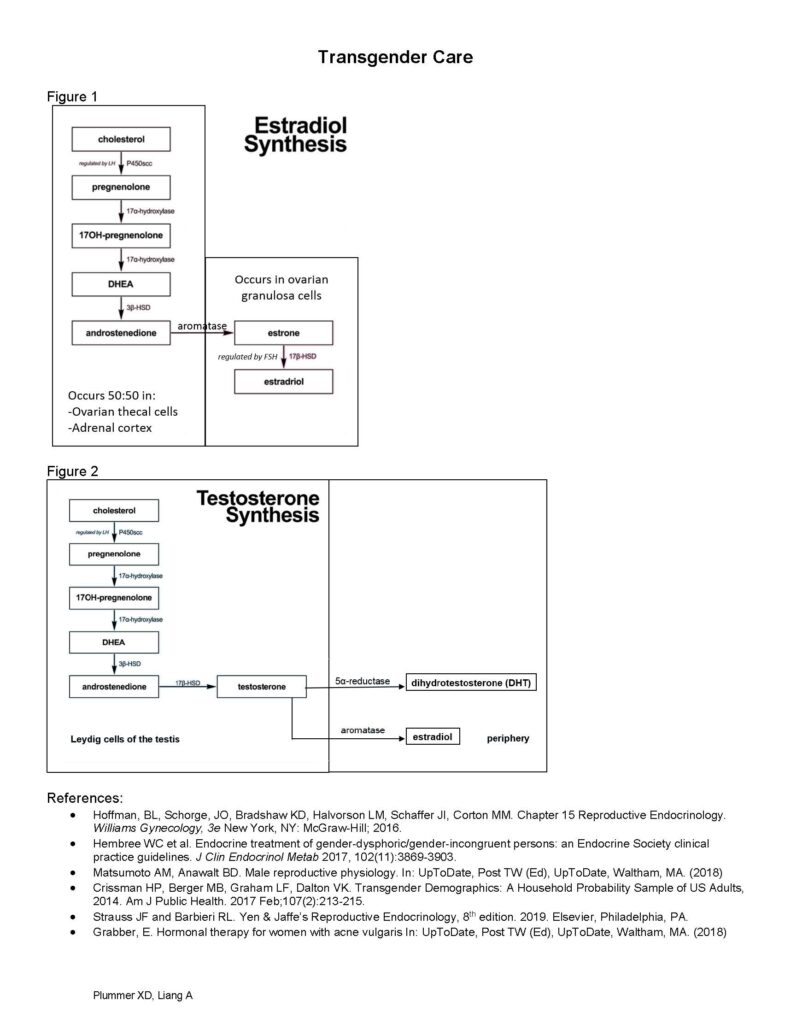
Synthesis: sex hormones are derived primarily from cholesterol and regulated by LH secretion (figures 1 & 2)
– cholesterol pregnenolone 17OH-pregnenolone DHEA androstenedione
– in females, this process occurs 50:50 in the adrenal gland and ovarian theca cells
– in males, this process occurs primarily in the Leydig cells of the testis
– androstenedione is then converted to estradiol or testosterone
– in females, regulated by FSH and occurs in ovarian granulosa cells: androstenedione aromatase estrone 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase estradiol
– in males, androstenedione 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase testosterone
In the periphery: Testosterone 5α-reductase dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
aromatase estradiol
What are the roles of estradiol and testosterone?
Estradiol is the major female sex hormone and responsible for:
– maintenance and development of primary female reproductive organs
– development of female secondary sexual characteristics
– regulating the female reproductive cycle
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone. In males, it is responsible for:
– development of male primary reproductive tissue
– development of secondary male sexual characteristics
What is the role of hormone therapy?
Male-to-female hormone therapy: primary goal is to both decrease testosterone and increase estrogen to female physiological range
– estradiol: acts on nuclear estrogen receptors to mediate gene transcription and promote:
– ↓body hair, ↓spontaneous erections, ↓muscle mass, redistribution of body fact, breast development
– Important to maintain below supra-physiological levels (<200pg/mL) secondary to thromboembolic risk & liver dysfunction
– antiandrogens: inhibits secretion and activity of testosterone which allows for ↓doses of estradiol therapy
– Spironolactone most common – blocks androgen receptors & decreases androgen synthesis
– Occasionally 5α reductase inhibitors (finasteride, dutasteride) are used
Female-to-male hormone therapy: goal is to increase testosterone to male physiological range
– testosterone: acts on nuclear androgen receptors to mediate gene transcription and promote:
– cessation of menses, ↑facial/body hair, ↑muscle mass, clitoromegaly, redistribution of fat, deepening of voice
What is the role of gender-affirming surgery?
– some patients may elect gender-affirming surgery which includes chest reconstruction surgery and reproductive/genital surgery
– surgeries are generally performed after long-term maintenance on hormone therapy by interdisciplinary teams involving gynecological surgeons, urologists and plastic surgeons as well as reproductive endocrinologists, primary care physicians, psychiatrists and psychologists Transgender Care
Plummer XD, Liang A
Figure 1
Figure 2
References:
Hoffman, BL, Schorge, JO, Bradshaw KD, Halvorson LM, Schaffer JI, Corton MM. Chapter 15 Reproductive Endocrinology. Williams Gynecology, 3e New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2016.
Hembree WC et al. Endocrine treatment of gender-dysphoric/gender-incongruent persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guidelines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017, 102(11):3869-3903.
Matsumoto AM, Anawalt BD. Male reproductive physiology. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (2018)
Crissman HP, Berger MB, Graham LF, Dalton VK. Transgender Demographics: A Household Probability Sample of US Adults, 2014. Am J Public Health. 2017 Feb;107(2):213-215.
Strauss JF and Barbieri RL. Yen & Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology, 8th edition. 2019. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA.
Grabber, E. Hormonal therapy for women with acne vulgaris In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (2018)